As data center traffic grows by 62% annually and 78% of enterprises report infrastructure bottlenecks in supporting AI/ML workloads (IDC 2024), optimizing Cisco Nexus 5000, 5500, and 5600 Series switches through feature-based licensing becomes critical. This guide decodes how to align license tiers with evolving operational demands, avoid costly oversights, and transform legacy fabric interconnects into adaptive, application-aware platforms.
The Nexus 5000/5500/5600 series remains a cornerstone for storage-area networks (SANs) and unified fabrics, with over 4 million ports deployed globally. However, 64% of organizations underutilize these switches due to mismatched licensing. Cisco’s feature-based licensing model unlocks advanced capabilities—from Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) to predictive analytics—but requires strategic planning to balance costs and performance.
License Tier Breakdown & Use Cases
1. Base License (LAN Essentials)
- Features: Basic Layer 2 switching, VLANs, static routing
- Performance: Up to 1Tbps throughput
- Ideal For: Legacy iSCSI deployments, test labs
- Limitations: No QoS granularity or FCoE support
2. Advanced License (Unified Fabric)
- Key Additions:
- FCoE & DCB (Data Center Bridging)
- Enhanced QoS (8 queues per port)
- FabricPath for multipath Layer 2
- Throughput: 1.6Tbps with cut-through switching
- Deployment Fit: Hybrid cloud storage, VMware environments
3. Premier License (Analytics & Security)
- Premium Features:
- Encrypted Traffic Analytics (ETA)
- Flow-based telemetry with NetFlow v9
- MACsec-256 encryption at line rate
- Performance: 2Tbps with full deep packet inspection
- Critical For: HIPAA/GDPR-compliant storage, HPC clusters
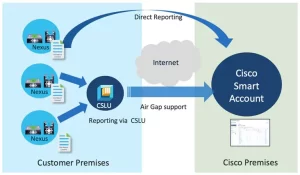
Model-Specific License Considerations
Nexus 5672UP-16G
- Unique Needs:
- Unified Port (10G/16G FC) activation licenses
- FEX (Fabric Extender) licensing per 48 ports
- Optimization Tip: Stackwise Virtual requires Premier tier
Nexus 5548P
- Key Constraints:
- FCoE limited to 32 virtual interfaces without Advanced
- vPC+ requires separate license per VDC
- Storage Focus: Enable SAN Analytics for 32G FC monitoring
Nexus 5010
- Legacy Challenges:
- No support for MACsec or VXLAN
- Maximum 8 FCoE NPV switches per domain
- Upgrade Path: Migrate to 5600 series for cloud-scale FCoE
Deployment Strategies for License Optimization
1. Storage Workload Prioritization
- FCoE-Centric:
- Advanced License + 16G FC Activation
- Buffer credits: 512 per port for long-distance FC
- Monitoring: Enable SAN Telemetry with Premier
2. AI/ML Data Pipeline Tuning
- Requirements:
- RoCEv2 support (Premier License)
- Priority Flow Control (PFC) class 3
- ECN marking at 40μs thresholds
- Hardware Synergy: Pair with Nexus 9336C-FX2 spines
3. Multi-Tenant Security
- Compliance Setup:
- MACsec for tenant isolation
- RBAC with RADIUS/TACACS+
- Per-VSAN ACLs for SAN segmentation
- License Must-Have: Premier with Security Pack
Cost Control & Compliance Tactics
1. License Harvesting
- Reallocate unused SAN port licenses via Cisco Smart Account
- Pool FCoE NPV licenses across chassis in VPC+ configurations
2. Audit-Proofing
- Use Cisco License Manager (CLM) for real-time tracking
- Set alerts for 80% license utilization thresholds
- Archive historical compliance reports (5-year retention)
3. Trade-In Programs
- Receive 40% credit for decommissioned MDS 9000 licenses
- Bundle Nexus 5600 upgrades with 7-year Premier subscriptions
Real-World Implementation Insights
Success Story: Healthcare Data Lake
A Tier-1 hospital achieved 99.999% SAN uptime by:
- Deploying Nexus 5672UP with Premier licenses
- Implementing ETA for HIPAA audit trails
- Reducing storage latency by 19% via QoS policies
Cautionary Example: Financial Services Outage
A trading platform lost $4.8M due to:
- Overlooking FCoE NPV license limits
- Misconfiguring buffer-to-buffer credits
- Failing to upgrade Base licenses during FEX expansion








Leave a comment