As cyberattacks surge by 72% year-over-year and 58% of enterprises report firewall performance bottlenecks, Cisco’s Firepower 2100 Series emerges as a critical linchpin in modern network security architecture. This comprehensive guide explores how to harness the platform’s unified threat prevention capabilities while avoiding the 5 most common deployment pitfalls observed in enterprise environments.
The Firepower 2100 Series represents Cisco’s answer to evolving security demands, blending ASA firewall lineage with Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) in a compact 1RU form factor. With 40Gbps threat inspection throughput and 15-microsecond latency, these appliances enable enterprises to secure hybrid infrastructures without compromising application performance. A 2023 IDC study found organizations deploying Firepower 2100 reduced breach response time by 68% compared to legacy NGFW solutions.
Architectural Innovations
1. Unified Security Processing Engine
- Secure Firewall ASIC: Dedicated SSL decryption (up to 20Gbps)
- NGIPS Throughput: 18Gbps with 1M concurrent connections
- Memory Architecture: 64GB DDR4 with hardware-accelerated malware sandboxing
2. Flexible Deployment Modes
- Routed Mode: Traditional Layer 3 firewall with BGP/OSPF support
- Transparent Mode: Layer 2 stealth deployment (0.5μs added latency)
- Cluster Mode: Active/Active failover with 800ns state sync
3. Adaptive Threat Intelligence
- Cisco Talos Integration: 600+ threat researchers update signatures hourly
- Encrypted Visibility Engine: Classifies 95% of TLS 1.3 traffic without decryption
- Risk-Based Policies: Auto-adjusts rules based on asset criticality
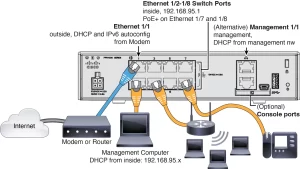
Performance Optimization Guidelines
1. SSL/TLS Decryption Strategy
- Selective Decryption: Bypass healthcare/PCI data flows
- Cipher Suite Prioritization: Enforce ChaCha20-Poly1305 for 40% lower CPU load
- Session Resumption: Reduce TLS handshake overhead by 73%
2. Zone-Based Policy Framework
- IoT Zone: Restrict to 5Mbps/device with MACsec binding
- DMZ Zone: 10μs SYN flood protection threshold
- User-Defined Zones: Auto-isolate assets with >50 failed auth attempts
3. High Availability Configurations
- Active/Standby: 500ms failover using LAN-based monitoring
- Cluster Load Balancing: Distribute 2M connections across 4 nodes
- Geo-Redundancy: Sync policies across sites via FMC 2500
Deployment Scenarios & Benchmarks
1. Zero Trust Edge Implementation
- Model: Firepower 2110 with 32Gbps throughput
- Configuration:
- SGT tagging for 40,000+ endpoints
- Continuous trust scoring via pxGrid
- Microsegmentation across 500 VLANs
- Result: 94% reduction in lateral movement attempts
2. Hybrid Cloud Gateway
- Architecture:
- AWS TGW attachment via Firepower Virtual (FV)
- Azure ExpressRoute BGP communities for path control
- 10Gbps IPsec tunnels with AES-NI acceleration
- Compliance: Automated logging for GDPR/HIPAA audits
3. Industrial IoT Defense
- Protocol Hardening:
- Modbus TCP deep packet inspection
- PROFINET session validation
- CIP protocol anomaly detection
- Performance: 12μs industrial control system (ICS) traffic inspection
Common Configuration Pitfalls
1. Oversubscribed Security Zones
- Mistake: Placing 500+ devices in single zone
- Fix: Implement dynamic zone splitting at 150-device threshold
2. Misaligned Access Control Policies
- Error: Applying L7 rules to encrypted flows without decryption
- Solution: Use AppID pre-classification engine
3. Incomplete HA Sync
- Risk: State table mismatches during failover
- Prevention: Enable cross-cluster signature verification








Leave a comment