In the high-stakes world of network operations, uptime isn’t just a metric—it’s a mandate. For organizations relying on Cisco’s Catalyst 2960-X, 2960-S, and 3750 series switches, power redundancy can mean the difference between seamless continuity and costly downtime. The Cisco Redundant Power System 2300 (RPS 2300) promises to eliminate single points of failure, but its value hinges on deployment context, budget, and risk tolerance. Is it a must-have for every network, or an overengineered solution for specific scenarios? Let’s dissect its role in safeguarding critical infrastructure.
The RPS 2300 Explained: Beyond Basic Backup
The RPS 2300 isn’t merely a backup power supply; it’s a centralized redundancy system designed to support up to six Cisco switches simultaneously. Key features include:
- Hot-Swappable Operation: Replace failed power supplies without interrupting connected switches.
- Multi-Device Support: One RPS unit can backfill power for six switches (e.g., three Catalyst 2960-X and three 3750s).
- Real-Time Monitoring: SNMP traps and Syslog alerts for power events via Cisco Prime Infrastructure.
However, its 1150W total output (192W per port) imposes limits. For example, a Catalyst 2960-X with a 715W PoE+ load would exhaust an RPS port, leaving no capacity for additional devices.
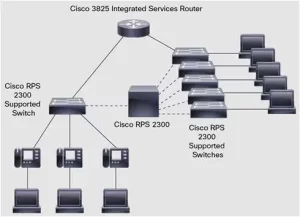
When RPS 2300 Becomes Non-Negotiable
1. Mission-Critical Environments
- Healthcare: A hospital’s ER network using Catalyst 3750 switches for patient monitoring systems.
- Risk: Power supply failure could delay critical data transmission.
- Solution: RPS 2300 ensures continuous uptime, meeting HIPAA uptime mandates (99.999%).
2. Distributed Enterprises with Limited IT Staff
- Retail Chains: 50+ stores relying on Catalyst 2960-S for POS and surveillance.
- Challenge: No on-site technicians to replace failed PSUs promptly.
- Solution: RPS 2300’s remote alerts and hot-swap capability minimize resolution time.
3. Budget-Constrained Redundancy
- SMBs: A manufacturer using Catalyst 2960-X for factory automation.
- Cost: Deploying RPS 2300 (12,000+).
- Savings: 79% reduction in redundancy costs.
The Hidden Limitations: When to Skip the RPS 2300
1. High-Power PoE Deployments
- Catalyst 2960-X with 715W PoE+: The RPS 2300’s 192W/port limit can’t fully backup a fully loaded switch.
- Alternative: Use internal redundant PSUs (e.g., C2960X-RPS) for high-power needs.
2. Modern Network Upgrades
- Legacy Hardware: The 3750 series entered Cisco’s End-of-Sale in 2015.
- Strategic Shift: Invest in newer Catalyst 9200/9300 switches with built-in redundancy instead.
3. Scalability Constraints
- Growing Networks: Adding a seventh switch? The RPS 2300 can’t expand beyond six devices.
- Workaround: Deploy multiple RPS units, but this increases complexity and cost.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Crunching the Numbers
| Scenario | Without RPS 2300 | With RPS 2300 |
|---|---|---|
| Downtime Cost/Hour | $10k (manufacturing) | $0 (failover <1s) |
| PSU Replacement Time | 4–48 hours (on-site visit) | 5 minutes (hot-swap) |
| 5-Year TCO (6 switches) | $18k (6x redundant PSUs) | $5k (RPS + maintenance) |
Case Study: A financial firm avoided $220k in potential trading losses during a PSU failure by using RPS 2300.
Alternatives to the RPS 2300
1. Internal Redundant PSUs
- Catalyst 2960-X-RPS: 600W internal redundancy, ideal for PoE-heavy setups.
- Pros: Dedicated per-switch backup.
- Cons: 2x cost per device vs. shared RPS.
2. UPS Integration
- APC Smart-UPS: Provides runtime during outages but doesn’t fix PSU failures.
- Best For: Short-term bridging until repairs.
3. StackWise Redundancy
- Catalyst 3750X Stacks: If one switch fails, others take over via StackWise Plus.
- Caveat: Doesn’t address individual PSU failures.
Deployment Best Practices
- Load Balancing: Distribute high-power switches (e.g., 3750-48P-S) across multiple RPS units.
- Monitoring Setup: Integrate RPS alerts with Splunk or ServiceNow for proactive IT responses.
- Lifecycle Alignment: Pair RPS 2300 with EoL switches only if upgrading within 2–3 years.








Leave a comment