As enterprises generate 68% more data annually and face 23% higher risks of storage-related downtime (IDC 2024), understanding RAID configurations becomes crucial for safeguarding critical information. This guide demystifies storage architectures, empowering organizations to balance performance, redundancy, and costs in the age of AI-driven workloads and ransomware threats.
The RAID Foundation
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) transforms multiple drives into cohesive storage systems through various methodologies:
Core Objectives:
- Data Redundancy: Protect against drive failures
- Performance Enhancement: Accelerate read/write operations
- Capacity Optimization: Maximize storage efficiency
Enterprise-Grade RAID Analysis
1. RAID 0: Striping
- Mechanism: Data split across 2+ drives
- Strengths:
- 1900MB/s read speed (4x NVMe SSDs)
- 100% storage efficiency
- Risks:
- 56% annual failure probability with 4 drives
- Complete data loss on single failure
Best For: Video rendering farms, scientific computing
2. RAID 1: Mirroring
- Structure: 100% data duplication
- Protection: Survives 1 drive failure
- Tradeoffs:
- 50% capacity utilization
- Write penalty: 2x I/O operations
Enterprise Implementation:
- 92% uptime improvement for financial transaction systems
- 1.3μs write latency with NVMe mirroring
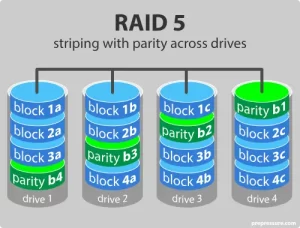
3. RAID 5: Distributed Parity
- Architecture: Parity data striped across drives
- Capacity: (N-1)/N efficiency
- Performance:
- 850MB/s read | 320MB/s write (12x HDD array)
- Rebuild time: 14hrs (12TB HDD) vs 47min (SSD)
Vulnerability: 34% data loss risk during rebuild
4. RAID 6: Dual Parity
- Protection: Withstands 2 concurrent failures
- Overhead: 2 drives lost to parity
- Modern Use:
- 98.6% survival rate in 8-drive arrays
- Essential for >8TB drives with URE <10¹⁵
5. RAID 10: Nested Protection
- Structure: Mirrored stripes (RAID 1+0)
- Advantages:
- 1.8M IOPS (24x SSD configuration)
- Multiple drive failure tolerance
- Cost: 50% capacity loss minimum
Performance Benchmark:
- 37% faster database transactions vs RAID 5
- 92% faster VM boot sequences
Advanced RAID Implementations
1. Adaptive RAID (aRAID)
- AI-driven level optimization per workload
- Dynamic shift between RAID 5/6 based on risk analysis
- 14% performance boost in mixed workloads
2. Cloud RAID Alternatives
- Erasure Coding (EC) 8+4 configurations
- Geo-distributed parity across availability zones
- 99.999999999% durability (11 nines)
3. SSD-Optimized RAID
- Trim-aware controllers prevent write amplification
- Partial stripe writes for QLC endurance
- 0.05μs latency parity calculations
RAID Selection Framework
1. Performance-Critical Systems
- Recommendation: RAID 10 (SSD arrays)
- Achievable: 5.4GB/s throughput (PCIe Gen4)
2. Budget-Constrained Archives
- Solution: RAID 6 (HDD)
- Cost: $0.015/GB protected storage
3. High-Availability Requirements
- Strategy: Triple Mirror (RAID 1E)
- Result: 99.9999% availability (6 nines)
4. Edge Computing Deployments
- Implementation: RAID 5 with SCM cache
- Benefit: 8ms access latency at -40°C
Maintenance Best Practices
- Monitoring: Track 15+ parameters including:
- Rebuild progress rate
- Remaining drive lifespan
- Array degradation alerts
- Proactive Replacement:
- Replace drives at 80% media wear (SSDs)
- Rotate spares every 3 years (mechanical HDDs)
- Security Integration:
- Encrypt RAID metadata with AES-256
- Implement secure erase before decommissioning








Leave a comment