What Is an API Gateway?
An API Gateway is a centralized API management and governance tool that streamlines how clients interact with backend services. Acting as the single entry point for all client requests, it routes traffic to the appropriate microservices, consolidates their responses, and delivers them back to the client. This setup eliminates the need for clients to directly communicate with multiple backend services, simplifying system interactions and enhancing security.
The API Gateway typically includes a range of capabilities such as configuration management, environment control, access authentication, user verification, and fine-grained access control. It enables enterprises to host, publish, and manage APIs in a secure, scalable, and cost-effective way.
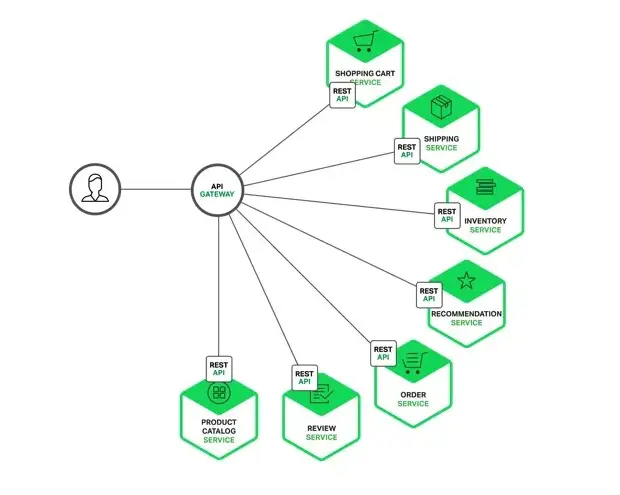
Why Do We Need an API Gateway?
The Rise of API Gateways
With the widespread adoption of microservices architecture, traditional monolithic applications have been decomposed into smaller, independently deployable services. While this architecture brings flexibility and scalability, it also results in the explosion of APIs, each with unique security, routing, and management needs.
As a result, managing and securing these APIs becomes increasingly complex. The API Gateway emerged to address these challenges by providing a unified platform to govern and manage APIs efficiently. Over time, its capabilities have expanded, making it an essential component of modern enterprise API ecosystems.
Key Benefits of an API Gateway
1. Centralized API Lifecycle Management
From design and development to testing, publishing, and decommissioning, an API Gateway supports the full API lifecycle, helping teams to build, manage, and scale APIs quickly and consistently.
2. Traffic and Rate Control
Built-in traffic management features allow you to define throttling rules, rate limits, and request quotas. These controls protect backend systems from overload and ensure consistent performance.
3. Real-Time Monitoring
API Gateways provide visual dashboards and real-time analytics, tracking key metrics such as latency, error rates, and usage patterns. This insight helps detect performance issues and potential security threats early.
4. Robust Security Measures
API Gateways enforce strict security protocols, including:
- Access control and user authentication
- IP blacklists/whitelists
- Anti-replay and anti-DDoS protections
- Role-based authorization
- Auditing and logging policies.
5. Flexible Routing and Deployment
Support for dynamic routing enables advanced deployment strategies like blue-green deployments and canary releases. Routing rules can be configured based on paths, headers, versions, or environments.
6. Multi-language SDK Support
Many API Gateways offer client SDKs in languages like Java, Go, Python, and C, simplifying integration across different application platforms without changing backend logic.
Core Functions of an API Gateway
1. API Aggregation
The Gateway can merge multiple microservices behind a single API, providing a unified interface to clients. This abstraction enhances system modularity and decouples frontend apps from backend complexity.
2. Intelligent Routing
Requests are forwarded to the appropriate backend services based on predefined rules. The gateway consolidates the responses before returning them to the client, enabling seamless cross-service interaction.
3. Traffic Management
It controls and distributes inbound traffic to maintain stability. This includes monitoring request rates, managing quotas, and detecting malicious behavior such as bot attacks or traffic spikes.
4. Unified Access Authentication
Instead of each microservice handling its own authentication, the API Gateway centralizes the process—reducing latency and improving consistency in access control.
5. Load Balancing
In high-traffic scenarios, the API Gateway can distribute requests across multiple service instances, improving fault tolerance and system availability.
6. Centralized Security Enforcement
The Gateway acts as a security shield, performing identity checks and input validation before requests reach internal systems. It also integrates with broader API management features like caching, monetization, filtering, and auditing.
Why choose API gateway?
| Consideration | Description |
| Performance | The API Gateway should efficiently handle a large number of concurrent API calls while maintaining low latency. |
| Reliability | It should have strong fault tolerance and disaster recovery mechanisms, ensuring redundancy and self-healing capabilities in case of node or service failure. |
| Security | Must offer comprehensive security features including authentication, authorization, protection against SQL injection, XSS, and DDoS attacks. Consider support for OAuth, JWT, and API keys. |
| Cost | Consider the budget. Open-source gateways can be attractive but may have hidden costs. Commercial gateways should be evaluated for total cost of ownership (TCO), including implementation and operational costs. |
| Community Support & Sustainability | Evaluate the community support and sustainability of the project or product to ensure long-term updates and assistance. |
| Usability & Management | Look for an API Gateway with easy configuration and user-friendly management interfaces. It should integrate with existing CI/CD pipelines and support automated deployment and management. |
| Scalability & Flexibility | The gateway should support horizontal and vertical scaling to accommodate business growth and changes. Check if it’s easy to add new services/features and allows for custom development. |










Leave a comment