Hello, everyone!
Why is GPON widely used?
Because broadband services require more bandwidth.
Introduction to GPON
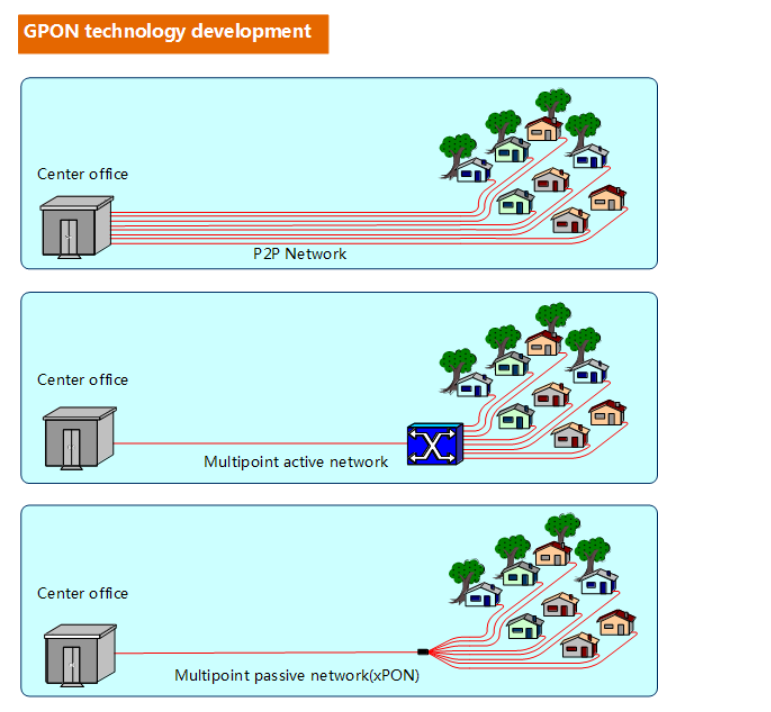
Passive Optical Network (PON) is a point to multi-point (P2MP) passive optical network. Mainstream PON technologies include broadband passive optical network (BPON), Ethernet passive optical network (EPON), and gigabit passive optical network (GPON). Adopting the ATM encapsulation mode, BPON is mainly used for carrying ATM services. With the obsolescence of the ATM technology, BPON also drops out. EPON is an Ethernet passive optical network technology. GPON is a gigabit passive optical network technology and is to date the most widely used mainstream optical access technology. GPON is defined by ITU-T Recommendation G.984.x.
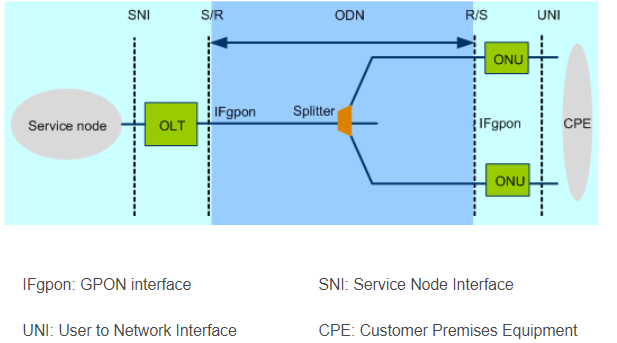
The optical line terminal (OLT) is an aggregation device located at the central office (CO) for terminating the PON protocol.
Optical network units (ONUs)/Optical network terminal (ONTs) are located on the user side, providing various ports for connecting to user terminals. The OLT and ONUs communicate with each other through the optical distribution network (ODN).
The optical distribution network (ODN) is composed of passive optical components (POS), such as optical fibers, and one or more passive optical splitters. The ODN provides optical channels between the OLT and ONUs. It interconnects the OLT and ONUs and is highly reliable.
Based on the preceding description, we can know some advantages of GPON:
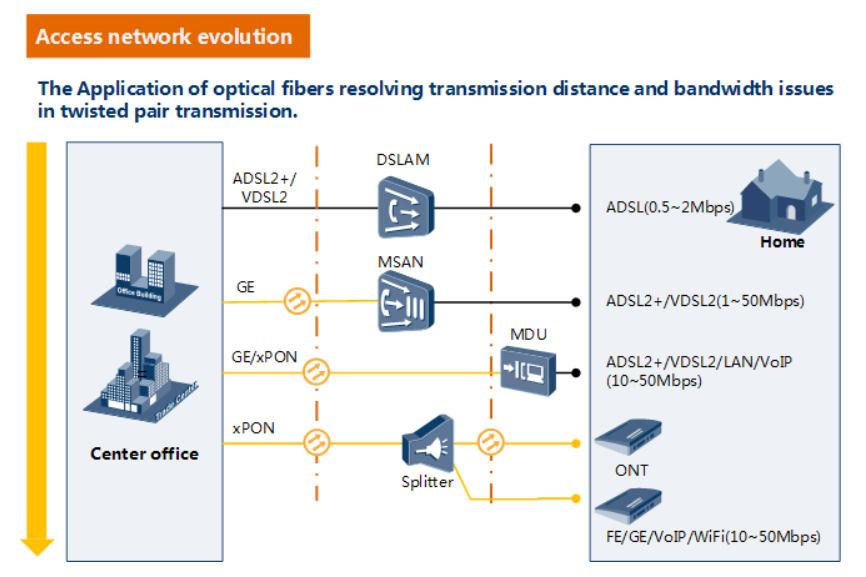
1:Longer transmission distance: The transmission media of optical fibers covers up to 60 km coverage radius on the access layer, resolving transmission distance and bandwidth issues in twisted pair transmission.
2:Higher bandwidth: Each GPON port can support a maximum transmission rate of 2.5 Gbit/s in the downstream direction and 1.25 Gbit/s in the upstream direction, meeting the usage requirements of high-bandwidth services, such as high definition television (HDTV) and outside broadcast (OB).
3:Flexible user experience on full services: Flexible QoS measures support traffic control based on users and user services, implementing differentiated service provisioning for different users.
4:Higher split ratio: GPON supports a split ratio up to 1:128. A feeder fiber from the CO equipment room can be split to up to 128 drop fibers. This economizes on fiber resources and O&M costs.
Thank you for reading!
Any ideas are welcome to leave a message. csd@telecomate.com








Leave a comment